Demand is strong. The real challenge is how quickly and cohesively U.S. plastics manufacturers can turn it into profitable production. Source: Stock
Household spending forms the bedrock of demand for molded plastic products in the U.S. economy. From everyday essentials like packaged goods and medical devices to durable items such as appliances, electronics and automobiles, consumer purchases cascade through supply chains, fueling orders for molded components from processors. Beyond tangible goods, service consumption — particularly in healthcare and travel — relies heavily on molded plastics for items like medical tubing, diagnostic equipment and luggage components. As these sectors demonstrate resilience amid 2025's economic headwinds, including a disruptive federal government shutdown, the outlook for molded plastics remains robust, with steady demand anchored in necessities rather than fleeting trends.
Lower interest rates in 2026 will help, and moderated tariff outcomes will reduce the worst-case pricing shock. Yet success will hinge on agile, well-coordinated responses.
Food and Beverage Spending Holds Firm
This year, the federal shutdown disrupted the usual flow of economic data, complicating real-time tracking of consumer spending spikes and dips by category. Yet, patterns in personal consumption expenditures (PCE) reveal a silver lining: spending on necessities has remained remarkably stable. Food and beverage consumption, a cornerstone for molded plastic packaging (e.g., bottles, containers and trays), hovered around $1.18 trillion in real terms during the first and second quarters of 2025, adjusted for inflation. By August, it climbed 2.0% year-over-year to $1.19 trillion, reflecting persistent demand for grocery staples.
Advance retail sales data from the U.S. Census Bureau further bolsters this stability, showing food and beverage store sales up 0.2% month-over-month and 2.7% year-over-year in September. These trends make a significant pullback in the third and fourth quarters unlikely, ensuring consistent orders for molded plastics in food processing and distribution. As inflation cools and supply chains normalize post-shutdown, this sector's reliability underscores molded plastics' role in essential, recession-resistant markets.
Demographics, Tech and AI Fuel Expansion
Healthcare services consumption, another voracious user of molded plastics (e.g., syringes, implants and ventilator parts), is poised for sustained growth, driven by an aging population and technological innovation. As a share of total personal consumption expenditures (PCE), healthcare expenditures rose to approximately 17.7% in August 2025, up from 16.9% in January 2023 — a trajectory accelerated by demographic shifts, where adults 65+ now drive disproportionate spending on chronic care and long-term services (see Chart 1).
This expansion signals enduring demand for molded plastics in the sector, far from fading amid economic uncertainty. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into healthcare is likely to further amplify this, elevating the share of medical services in overall consumption. By enhancing diagnostic precision — such as achieving 87-90% accuracy in early disease detection — enables proactive interventions, transforming optional or reactive care into essential, preventive and personalized strategies. This shift reinforces healthcare as a structural imperative rather than a discretionary outlay, potentially adding 7-9% to national health expenditures through expanded utilization.

Vehicle Sales Defy Headwinds
Molded plastics are ubiquitous in automobiles and light trucks, from interior trims and dashboards to under-hood components and EV battery housings. Despite elevated financing costs and looming tariffs that threatened double-digit price hikes, monthly U.S. light-vehicle sales remained above 15 million units on a seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) throughout 2025. A pre-tariff rush propelled sales to a peak of 17.9 million in March, dipping to 15.6 million in May before rebounding above 16 million in July, August and September, and settling at 15.6 million in November (see Chart 2).
Only 3.63% of U.S. workers relied on public transportation for commuting in 2024, per Census data — a figure underscoring the entrenched preference for personal vehicles. While shifts in vehicle composition (e.g., from internal combustion engines to EVs) may alter material mixes, overall demand shows no signs of abating. With employment as the primary source of income for most households and a resilient labor market, light-vehicle purchases are expected to remain robust.
September's unemployment rate of 4.4% — below the natural rate of 4.9% estimated by the Federal Reserve and Congressional Budget Office — highlights this stability, even as softening signals emerge. Philadelphia Fed projections anticipate 4.2% unemployment in 2025 and 4.5% in 2026, still sub-5.0% levels conducive to consumer mobility.
Fluctuations Amid Uncertainty
Consumer sentiment ebbed and flowed in 2025, buffeted by tariff anxieties and economic flux. The University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index logged more month-over-month declines than gains over the past 12 months, dipping from 74.0 in December 2024 to a near-record low of 51.0 in November 2025 — a 31% plunge. This reflects mounting worries over inflation, job security and fiscal pressures, prompting households to recalibrate spending toward essentials while trimming discretionary outlays.
Yet, such volatility is par for the course: Confidence indices naturally oscillate as consumers adjust balance sheets to evolving conditions, from interest rates to policy shifts. The index's forward-looking tilt suggests potential stabilization if inflation eases further, but persistent below-70 readings signal caution in non-essential categories; though molded plastics in durables like autos and appliances benefit from their semi-essential status.
Credit Access Tightens
Compounding these dynamics, consumer debt burdens have intensified as credit conditions have hardened. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York's data shows overall credit rejection rates climbing to a series high of 24.8% in October 2025, up from 23.1% in June and well above 2024 levels. This encompasses home loans, auto loans and mortgage refinancings, where denials surged amid affordability strains. The share of discouraged borrowers — those sidelined by rejection fears — rose to 8.0% from 7.2% in June and 6.6% in October 2024, signaling broader caution.
These trends could temper big-ticket purchases like vehicles, yet they also highlight a pivot to necessities, where molded plastics thrive. As lenders tighten amid elevated delinquencies, consumers lean on reliable, lower-cost items, sustaining demand in core sectors.
Household spending's focus on essentials — from stable food packaging to expanding healthcare and steady auto demand — positions molded plastics for continued vitality.
Plastics' Role in a Resilient Economy
In 2025, household spending's focus on essentials — from stable food packaging to expanding healthcare and steady auto demand — positions molded plastics for continued vitality. While shutdown disruptions, tariff threats and credit squeezes introduce volatility, structural drivers like demographics, AI innovation and a sub-5% unemployment rate ensure demand's persistence. As consumers navigate uncertainty, molded plastics remain indispensable, bridging everyday needs and future-oriented sectors. For industry stakeholders, the message is clear: Bet on resilience, not recession.
Despite the underlying resilience in U.S. household spending throughout 2025, the manufacturing sector’s reaction, particularly in molded plastics and related industries, has been uneven and cautious. While consumer demand for essentials and semi-durables has held steady, manufacturers have faced a confluence of higher interest rates, tariff uncertainty and lingering yield-curve inversion effects that have tempered investment and delayed new projects.
Positive, Yet Volatile New Orders
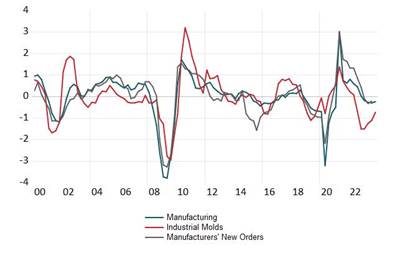
From January through September 2025, year-over-year growth in manufacturers’ new orders remained in positive territory, the first sustained stretch above zero since the post-COVID volatility subsided. The strongest reading came in May at +9.7%, fueled by pre-tariff inventory buildup and robust retail restocking. Growth then moderated sharply to +1.6% in July amid heightened policy uncertainty, before recovering modestly to +3.7% in August and +3.6% in September.
Over the past decade (excluding the extreme swings of 2020–2023), 12-month momentum in new orders has rarely strayed beyond the −10% to +10% corridor. The current cycle fits this historical pattern, but the backdrop is notably different: an inverted yield curve that began in mid-2022 has consistently preceded softening order growth — a relationship that held true again this year (see Chart 3).
Interest Rates and Capital Allocation Discipline
The Federal Reserve’s aggressive tightening cycle pushed the upper bound of the federal funds rate to 5.50% in 2023-2024 and the Industrial Production Index for plastics products manufacturing began contracting precisely when that ceiling crossed 4.0%. At elevated borrowing costs, new tooling and capacity-expansion projects require significantly higher expected returns on capital to justify investment. As a result, many processors postponed product-line extensions, new mold programs and greenfield facilities; opting instead for sweat-the-assets strategies and selective maintenance capex.
With two 50-basis-point cuts already delivered in 2025, the funds rate now stands at 3.75-4.00% and markets are pricing in a high probability of another cut at the December Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting that would bring the range to 3.50-3.75%. Lower financing costs, if sustained into 2026, should gradually unlock deferred projects and support a more confident capital-spending cycle.
Mixed Blessings and Ongoing Uncertainty
Higher tariffs on imported goods and raw materials, particularly steel, aluminum and downstream derivatives, have delivered a mixed impact. On one hand, they have provided a measurable lift to domestic manufacturing activity: overall manufacturing industrial production posted its strongest year-over-year gain of the cycle at +3.5% in September, rebounding from a −0.4% decline in March. On the other hand, the initial fear of double-digit price spikes across finished goods has not materialized, as trading partners negotiated phased or reduced reciprocal tariffs.
For the molded-plastics ecosystem, this outcome preserves import competition in molds, resins and finished components while granting U.S. producers a modest “home-court” cost advantage. However, the advantage is far from decisive. Intensified domestic reshoring and new entrants looking to skirt tariffs could actually heighten competition on American soil in the coming years.
As consumers navigate uncertainty, molded plastics remain indispensable, bridging everyday needs and future-oriented sectors. For industry stakeholders, the message is clear: Bet on resilience, not recession.
The Path Ahead
The central challenge for U.S. molded-plastics manufacturers is no longer simply whether consumer demand will remain supportive — it clearly has — but how quickly and cohesively the industry can translate that demand into profitable investment and production. Lower interest rates in 2026 will help, and moderated tariff outcomes will reduce the worst-case pricing shock. Yet success will hinge on agile, well-coordinated responses, including rapid tooling development for new programs, disciplined capacity planning and close collaboration across the supply chain to capture share before new domestic competitors come fully online.
In short, 2025 was a year of jagged progress rather than outright retreat. As monetary policy eases and trade policy stabilizes, the stage is set for a more constructive chapter — one where resilient household spending finally meets a more confident and synchronized manufacturing response.
Related Content
Tooling 4.0: Connecting Industry 4.0 Technology to Your Molds and Molding Process
A packaging supplier applies Industry 4.0 technology to its injection molds so that components talk to each another to understand the dynamics of what is happening inside the mold.
Read MoreMMT Chats: Championing Moldmaking Recruitment
Production manager is doing his part to help transform skilled trades recruitment through strategic advocacy and digital engagement.
Read MoreMaking Mentoring Work | MMT Chat Part 2
Three of the TK Mold and Engineering team in Romeo, Michigan join me for Part 2 of this MMT Chat on mentorship by sharing how the AMBA’s Meet a Mentor Program works, lessons learned (and applied) and the way your shop can join this effort.
Read MoreMMT Chats: One Moldmaker’s Mission Empowers Veterans
Don Starkey helps lead iWarriors, a volunteer-run nonprofit gifting iPads to injured veterans for connection, recovery and independence.
Read MoreRead Next
Moldmakers in a Shifting Economy: Consumption Trends, Tariff Impacts and Production Outlook
U.S. mold imports are rising despite tariffs, showing strong demand as moldmakers face cost pressures, policy uncertainty and new opportunities from shifting manufacturing and consumption trends.
Read MorePutting US Manufacturing on High Gear: Are Moldmakers Caught in the Middle?
Requirements for expanding domestic manufacturing footprint and moldmaker considerations when adapting to the evolving industry landscape.
Read MoreNavigating Economic Resilience and Consumer Trends
Consumer behavior provides mold builders insight into the evolving market dynamics of goods and services that helps strategic planning.
Read More